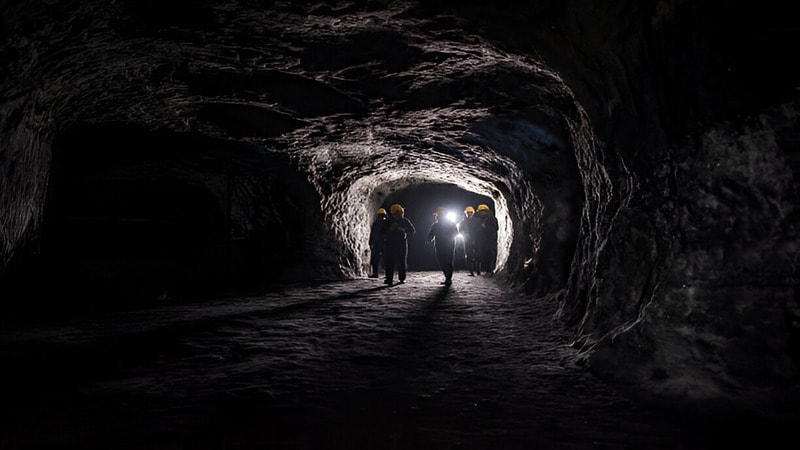
Coal is one of the world’s most important energy sources, and much of it comes from deep underground. Countries like China, India, the United States, and Australia rely heavily on underground coal mining to meet their energy needs.
You won’t believe it but over 60% of China’s coal is mined using underground methods. But how does underground coal mining work? What machines are used? How do miners stay safe hundreds of meters below the surface?
In this guide, we’ll explain how underground coal mines operate and key safety practices. We’ll also introduce important equipment like gas extraction drilling rigs and highlight new technologies that are making mining smarter and safer.
What is Underground Coal Mining
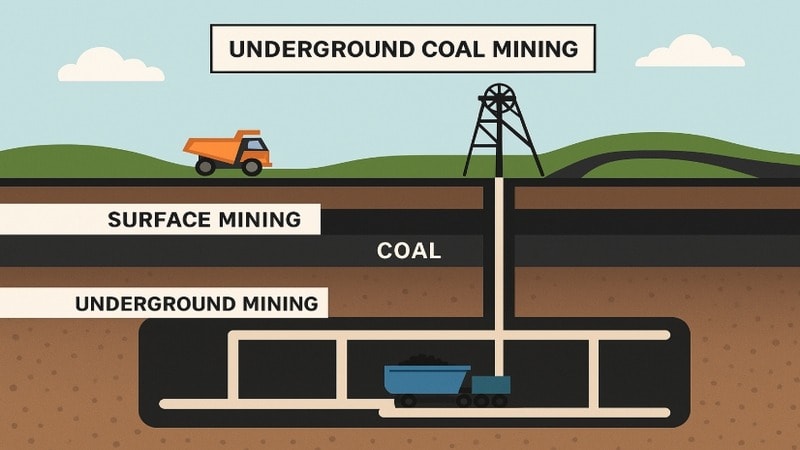
Underground coal mining is the process of extracting coal from deep beneath the earth’s surface. It uses methods like blast hole drilling, continuous miner machines, and drilling rigs to reach and remove coal seams.
Shafts and tunnels are constructed to access the coal, and equipment like rock bolts helps keep the area stable. This method is used when coal is too deep for surface mining and requires careful planning for safety, production, and cost control.
In Australia’s Appin Mine, coal is mined from over 600 meters below ground using longwall mining machines. These machines can extract hundreds of tons of coal per hour, showing how powerful and efficient underground mining methods can be.
Here’s why choosing underground coal mining can be a smart decision:
- Allows access to deep coal seams not reachable by surface mining
- Maintains a consistent production cycle in complex geological conditions
- Uses advanced equipment like drilling rigs and continuous miners for efficient operation
- Involves blast hole drilling and controlled blasting for precise coal extraction
- Improves safety with the use of rock bolts and proper ventilation systems
- Reduces risk of surface subsidence and protects nearby underground utilities
Surface Coal Mining vs. Underground Coal Mining
The difference between subsurface coal mining and surface coal mining lies in how minerals are extracted from the earth.
| feature | Surface Mining | Underground Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Depth of Coal | Shallow (less than 200 feet) | Deep (can be over 1,000 feet) |
| Environmental Impact | More surface disruption | Less visible surface impact |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | More expensive due to complexity |
| Coal Recovery Rate | Higher in some methods | Depends on the method used (e.g., Longwall can be high) |
| Use Case | Flat terrain with shallow coal seams | Mountainous or urban areas with deep seams |
Underground Drilling and Extraction Methods
Underground coal mining employs various drilling and extraction methods to reach coal seams beneath the earth’s surface efficiently. Each method is chosen based on factors such as coal seam depth, geological conditions, safety concerns, and production targets. Below are the primary techniques used in subsurface mining:
Room and Pillar Mining
Room and pillar mining is one of the oldest and most widely used underground coal mining methods. It involves creating a series of tunnels or “rooms” to extract coal while leaving “pillars” of coal to support the mine roof. This method is typically used in flatter coal seams and is known for its ability to balance coal recovery and mine stability.
Longwall Mining
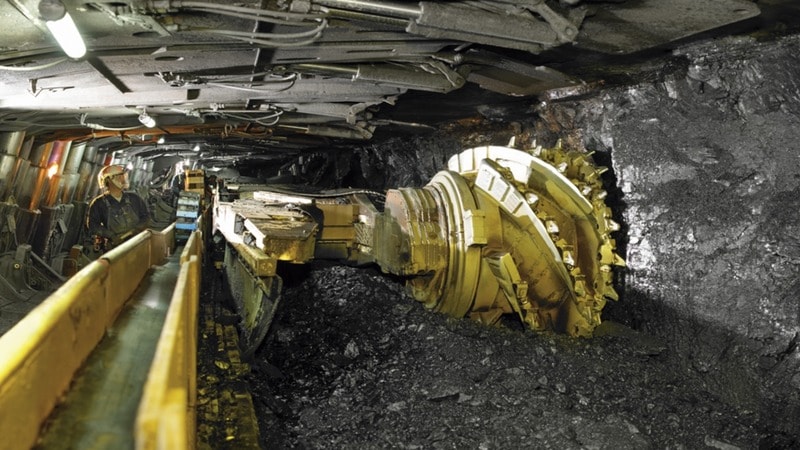

Longwall mining is a highly automated method that involves using a longwall shearer to cut a continuous slice of coal along the full width of a coal seam. As the shearer moves along the seam, the mined coal is transported via a conveyor system to the surface
Continuous Miner Mining
Continuous mining uses a continuous miner machine to cut and gather coal from the face of the mine. This method is used for thinner seams where longwall mining is not feasible. The continuous miner cuts a path through the coal and loads it directly onto a conveyor system for transport.
Cut and Fill Mining
Cut and fill mining is a method for mining steeply dipping or irregularly shaped coal seams. It involves removing coal in stages, beginning with the top portion of the seam and filling the void with waste material to stabilize the mine. This method is often used in conjunction with other techniques, such as room and pillar, in difficult conditions.
Blast Hole Drilling and Blasting
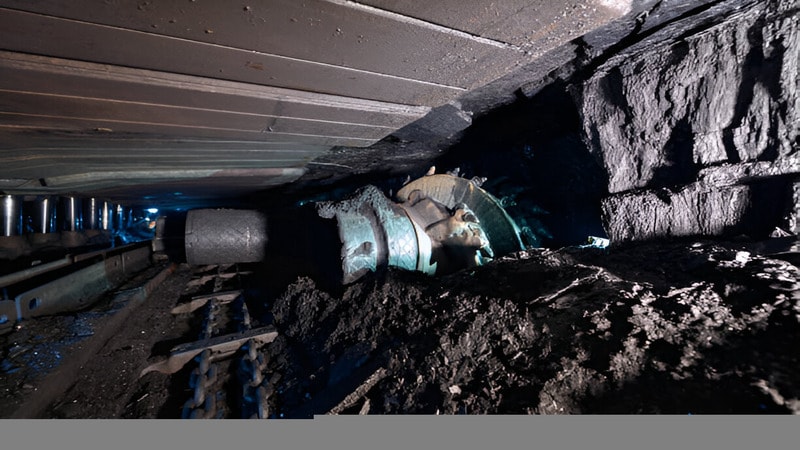

In some underground coal mines, blast hole drilling creates holes in the coal seam. Explosives are then placed in these holes to break the coal into smaller, manageable pieces for extraction. This method is more commonly used in areas where the coal is embedded in hard rock.
Essential Coal Mining Safety Equipment
Coal mining requires specialized safety equipment to protect workers from potential hazards. The key components include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This includes items such as hard hats, safety goggles, hearing protection, flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection to shield workers from falling debris, noise, dust, and gases.
- Team Safety Gear: In addition to individual PPE, mining teams are equipped with safety harnesses, lifelines, and gas detectors to ensure safe movement and to monitor hazardous gases in underground environments.
These tools are crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring a safe working environment in both underground and surface coal mines.
Drilling and Blasting Techniques
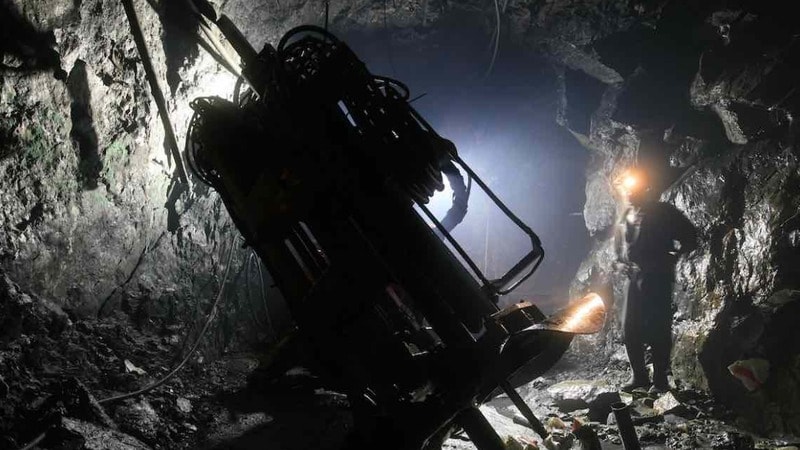

Drilling and blasting are still the most effective ways to break up rugged rock and access deep coal seams. This technique is about precision and control—especially when working hundreds of meters underground where space is tight, and safety is critical.
So, what exactly happens? It starts with blast hole drilling, where miners use specialized equipment to drill deep holes into the coal or surrounding rock. These holes are then carefully filled with controlled amounts of explosives. Once everything is set and checked multiple times, the blast is triggered.
The explosion breaks apart the coal, making it easier for other machines to scoop it up and transport it to the surface. But don’t think this is just about blowing things up—it’s a science. Everything from the holes’ spacing to the blast’s timing is calculated to reduce vibration, limit dust, and protect both workers and equipment.
Blasting is especially useful in:
- Areas with hard rock
- Seams that are too deep or irregular for machines alone
- Mines where efficiency is key, and time is money
With modern technology, this process has become much smarter. Digital blast design tools and remote monitoring systems are now commonly used to keep operations smooth, safe, and effective.
Underground Drilling Rigs for Coal Mining

You can’t talk about underground mining without talking about underground drilling rigs. They speed up the productivity by up to 30%. Additionally, these machines do more than dig holes—they support almost every stage of a coal mine’s life cycle.
Need to check the quality of a coal seam before mining starts? Use a drilling rig. Need to reduce dangerous methane gas before workers go in? Drilling rigs again. Want to make sure the ceiling of a tunnel doesn’t collapse? Yes, that’s the role of drilling rigs, too.
There are different types of rigs for different jobs:
- Exploration rigs help geologists study the coal before mining.
- Gas drainage rigs remove methane and other gases that can build up and cause explosions.
- Roof bolting rigs drill into rock to install support bolts, keeping tunnels stable.
A good drilling rig boosts safety, speeds up mining, and reduces downtime. Picking the right drilling rig depends on factors like how deep the coal is, the surrounding rock’s condition, and the mine’s size and layout.
Introduction to Tunnel Drilling Rigs
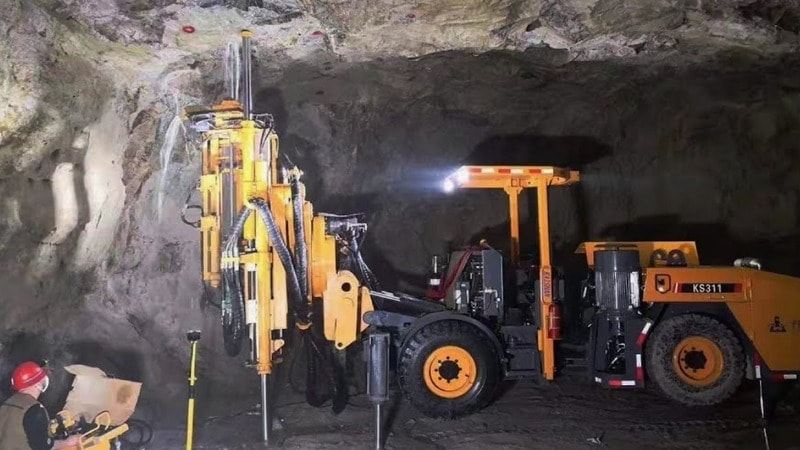

Tunnel drilling rigs are the underground heroes of coal mining. These machines don’t just drill straight down—they can move at angles, curves, and even horizontal paths. That’s why they’re perfect for creating long underground tunnels, ventilation paths, and access roads.
A key feature of tunnel drilling rigs is their use of directional drilling technology. This technology enables the rig to follow the path of the coal seam, regardless of its twists and turns. These rigs are primarily used for tasks such as:
- Gas drainage boreholes in coal mines
- Coal seam water injection holes
- Roof pressure relief holes
- Geological exploration and water detection boreholes
Additionally, they excel at cross-seam drilling in both high and low gas drainage roadways, in-seam drilling along airways, and advanced probing ahead of tunneling faces. This wide range of capabilities makes tunnel drilling rigs a critical tool for improving safety and efficiency in mining operations.
Here’s how tunnel drilling rigs are advancing mining operations:
- They access areas that are too dangerous or difficult for humans or other machines to reach.
- They help eliminate harmful gases before mining begins, making the site safer for workers.
- They reduce the need for new surface entry points, helping to protect the environment and reduce operational costs.
With the integration of remote-control systems and automated drilling technology, these rigs can operate with minimal human presence in high-risk zones, further enhancing safety and efficiency.
Advanced technology: Underground Directional Drilling Technology
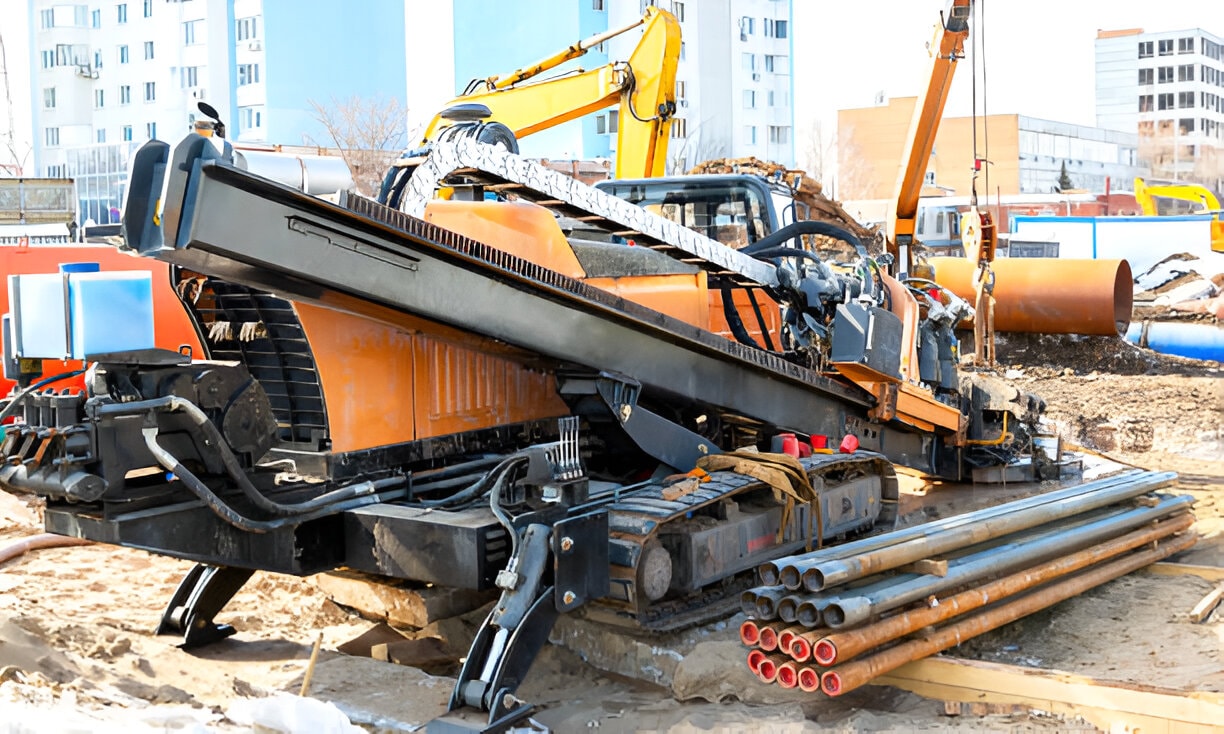

If tunnel drilling rigs are the heroes, directional drilling is their superpower. This technology allows miners to steer the drill bit with extreme accuracy underground—like a GPS for drilling.
Instead of only going straight down, directional drilling lets the machine move sideways, curve around obstacles, and even follow the exact shape of a coal seam.
Why is this important?
- It helps drain gas from coal seams before mining starts, which makes the work area much safer.
- It lets miners access more coal without damaging the environment above ground.
- It allows teams to work in complex or narrow areas where traditional methods would fail.
Directional drilling is now used in many modern coal mines, especially where safety and environmental protection are top priorities. It’s also a key tool in gas exploration, helping remove dangerous methane while increasing coal recovery.
So, if you picture coal mining as dark tunnels and heavy machines, directional drilling is the quiet, clever tech running behind the scenes—making everything run smoother, safer, and more efficiently.
Gas Extraction and Gas Drainage of Coal Seams: Why It Matters
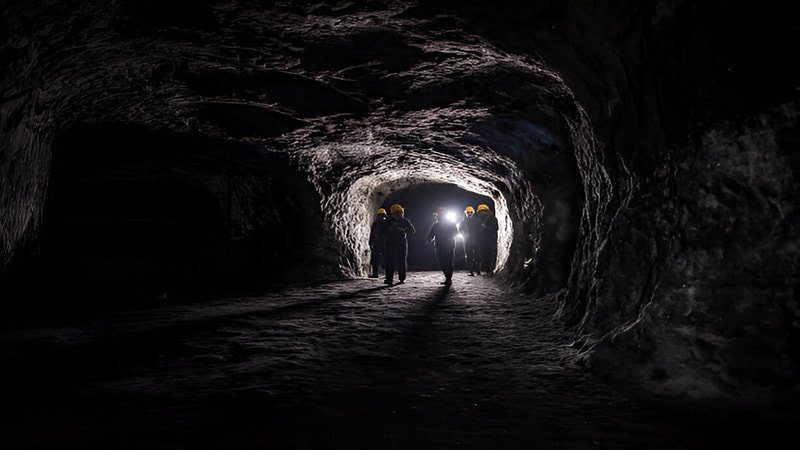

Gas hazards in coal seams, mainly methane, pose a serious risk to mining operations. Methane is highly explosive, and even low concentrations (5-15%) can lead to dangerous explosions. Proper gas extraction and drainage techniques are essential to ensure safe mining.
Gas extraction involves removing methane from coal seams before mining starts. This helps reduce methane buildup and lowers the risk of explosions. Specialized gas extraction drilling rigs create boreholes in the coal seam and safely vent methane to the surface.
Several methods are used to drain gas from coal seams, includes:
- Vertical Boreholes: Drilled vertically to extract gas from the coal seam.
- Horizontal In-Seam Drilling: Drilling horizontally to reach deeper gas pockets.
- Cross-Measure Boreholes: Drilling across the seam to remove gas from different sections.
- Surface-to-In-Seam Directional Drilling: Precision drilling from the surface to target gas-rich areas.
- Gas Drainage During Mining: Removing gas as mining progresses.
- Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking): Injecting fluid under pressure to release trapped gas.
Proper gas drainage is essential for both safety and environmental compliance. Miners can avoid explosions and maintain a safer working environment by controlling methane levels. Additionally, adequate gas drainage helps companies meet regulations around methane emissions and reduce the environmental impact of mining.
Ventilation Systems in Underground Coal Mining
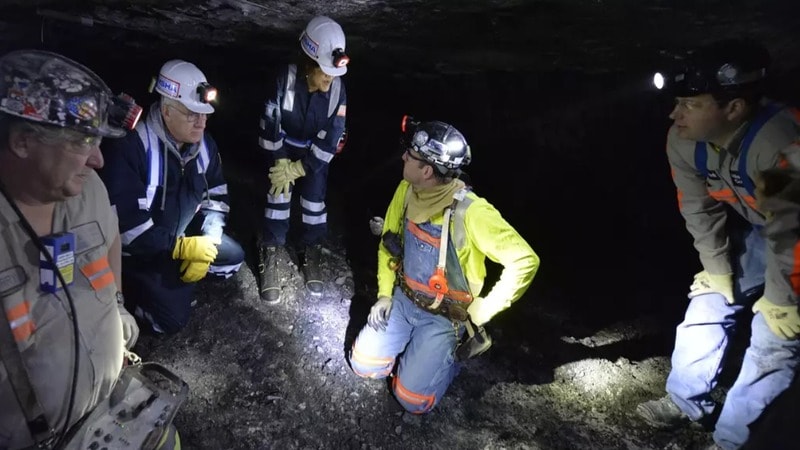

Ventilation is one of the most vital aspects of underground coal mining. Harmful gases like methane and carbon monoxide can build up without proper airflow, creating hazardous conditions. A sound ventilation system ensures miners have fresh air to breathe while preventing dangerous gas explosions.
Following are the basic components of a ventilation system:
- Fans and Airflow Systems: These provide fresh air to the mine and remove stale air and gases.
- Airshafts: Vertical shafts help bring air into the mine and release harmful gases.
- Doors and Regulators: Control the airflow direction and ensure air reaches all mine sections.
Transportation Systems in Underground Coal Mining
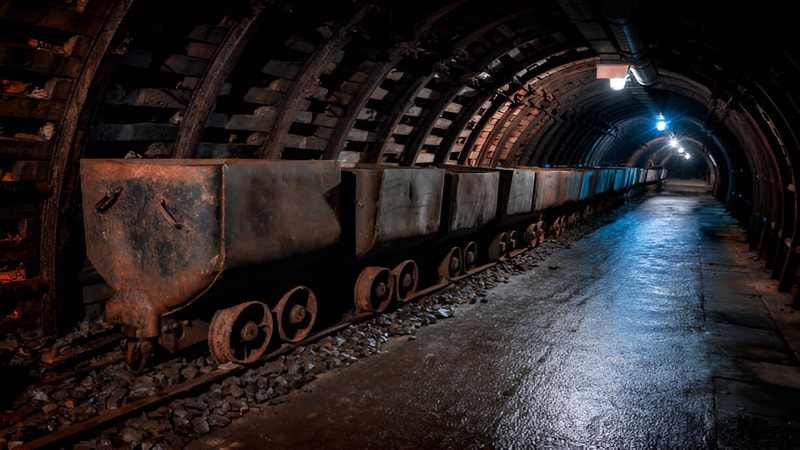

Transporting coal and materials within a mine is critical for efficiency. Without an effective transportation system, moving coal from the extraction point to the surface would be slow and costly. There are several key transportation systems used in underground coal mining.
- Rail Systems: Trains move coal and materials through tunnels. They’re effective for transporting large amounts of coal over longer distances.
- Conveyor Belts: These automated systems move coal continuously from the mine face to the surface. They are cost-effective and fast.
- Shuttle Cars: Small vehicles that transport coal from the mine face to larger conveyor systems or the mine’s main shaft.
A well-designed transportation system keeps operations running smoothly. It ensures coal is moved efficiently, minimizes delays, and helps maintain the mine’s overall productivity.
Selecting Appropriate Equipment and Technologies
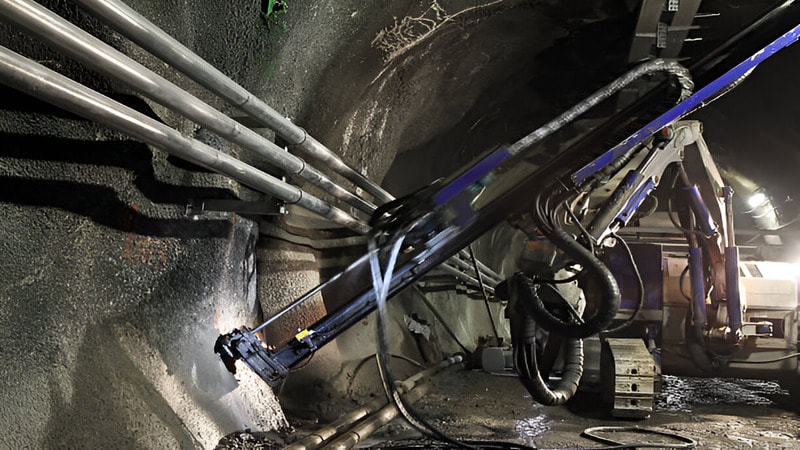

When choosing equipment for underground coal mining, factors like the depth of the seam, the area’s geology, and the type of mining (longwall or room and pillar) must be considered. The equipment must be efficient, durable, and tailored to the mine’s needs.
Mining equipment operates in harsh conditions. Reliable equipment and regular maintenance are crucial to avoid costly downtimes. Keeping machines in good condition ensures they operate efficiently and safely.
Mining technology is rapidly evolving. Innovations like autonomous vehicles, AI-powered monitoring systems, and improved ventilation systems are making mining operations more efficient, safer, and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
Underground coal mining involves powerful machines, careful planning, and a strong focus on safety. As the industry grows, new technologies and methods make mining more efficient, safer, and environmentally friendly. Everything from drilling to ventilation systems is designed to ensure the workers’ safety and the protection of the environment.
Start Your Mining Journey with HWDrill
If you want to learn more about underground coal mining or need help with the latest equipment and techniques, do check out Hwdrill. Our team is ready to help you find the best solutions for your mining needs. Contact us and let’s work together to make mining smarter and safer!




